Презентация Мобильные сотовые сети онлайн
На нашем сайте вы можете скачать и просмотреть онлайн доклад-презентацию на тему Мобильные сотовые сети абсолютно бесплатно. Урок-презентация на эту тему содержит всего 64 слайда. Все материалы созданы в программе PowerPoint и имеют формат ppt или же pptx. Материалы и темы для презентаций взяты из открытых источников и загружены их авторами, за качество и достоверность информации в них администрация сайта не отвечает, все права принадлежат их создателям. Если вы нашли то, что искали, отблагодарите авторов - поделитесь ссылкой в социальных сетях, а наш сайт добавьте в закладки.
Презентации » Технология » Мобильные сотовые сети
Оцените!
Оцените презентацию от 1 до 5 баллов!
- Тип файла:ppt / pptx (powerpoint)
- Всего слайдов:64 слайда
- Для класса:1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
- Размер файла:3.38 MB
- Просмотров:63
- Скачиваний:0
- Автор:неизвестен
Слайды и текст к этой презентации:
№2 слайд
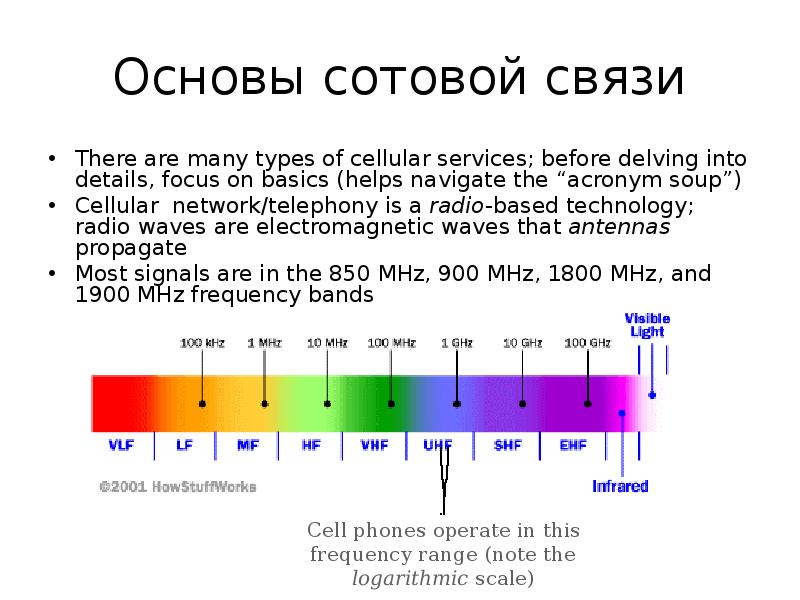

Содержание слайда: Основы сотовой связи
There are many types of cellular services; before delving into details, focus on basics (helps navigate the “acronym soup”)
Cellular network/telephony is a radio-based technology; radio waves are electromagnetic waves that antennas propagate
Most signals are in the 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequency bands
№3 слайд
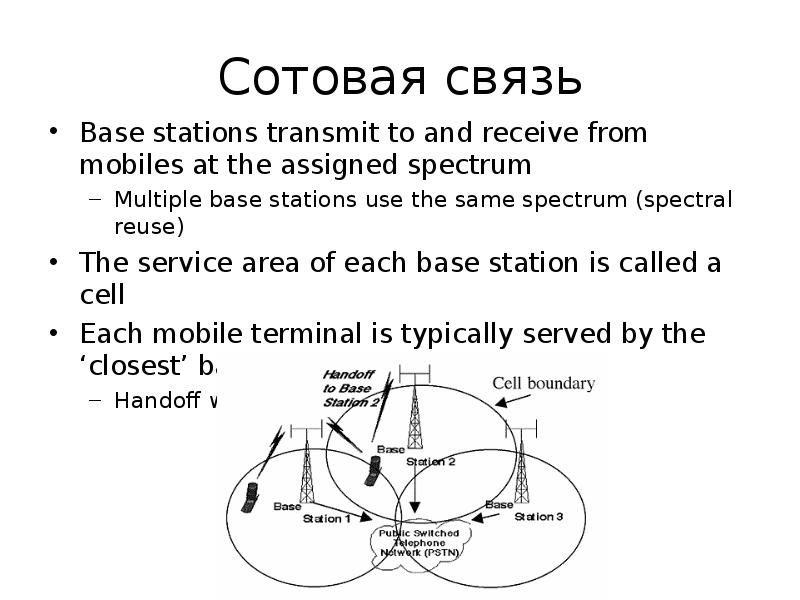

Содержание слайда: Сотовая связь
Base stations transmit to and receive from mobiles at the assigned spectrum
Multiple base stations use the same spectrum (spectral reuse)
The service area of each base station is called a cell
Each mobile terminal is typically served by the ‘closest’ base stations
Handoff when terminals move
№4 слайд


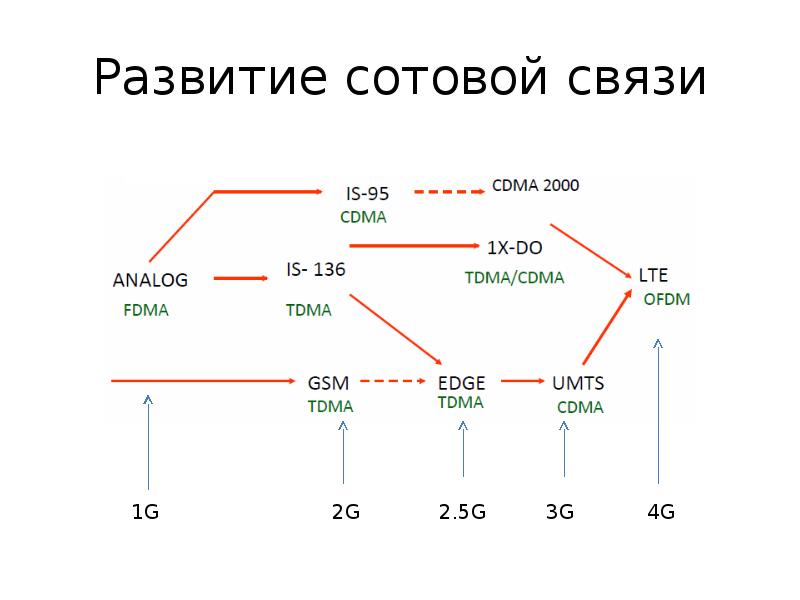
Содержание слайда: Поколения сотовой связи
It is useful to think of cellular Network/telephony in terms of generations:
0G: Briefcase-size mobile radio telephones
1G: Analog cellular telephony
2G: Digital cellular telephony
3G: High-speed digital cellular telephony (including video telephony)
4G: IP-based “anytime, anywhere” voice, data, and multimedia telephony at faster data rates than 3G
(to be deployed in 2012–2015)
№6 слайд


Содержание слайда: Проблема
Множественного Доступа
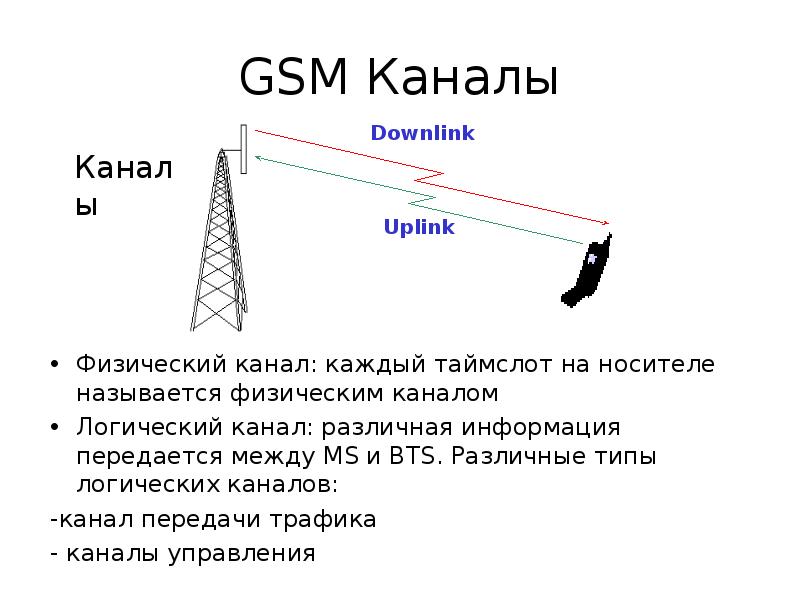
Базовые станции должны обслуживать множество мобильных терминалов одновременно (both downlink and uplink)
Все мобильные телефоны в соте нужны для передачи к базовой станции
Интерференция между различными отправителями и получателями
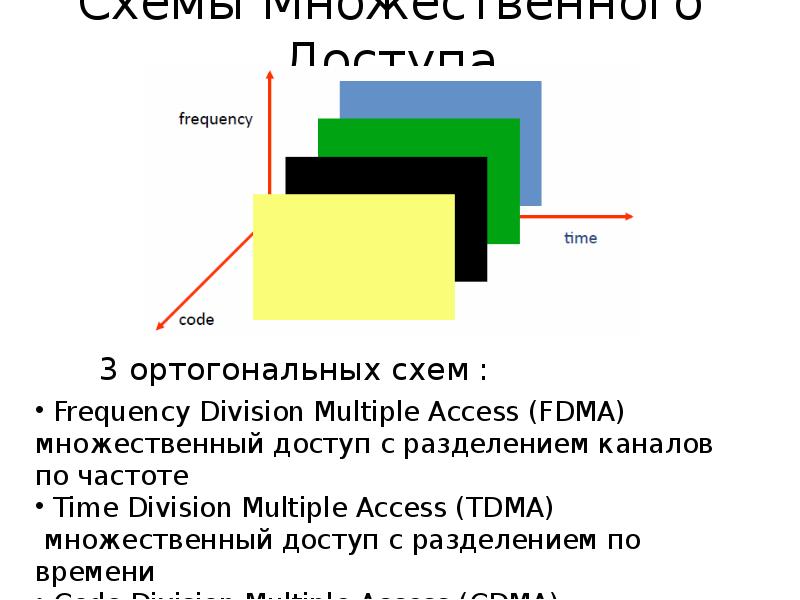
Поэтому нужна схема множественного доступа
№8 слайд


Содержание слайда: множественный доступ с разделением каналов по частоте
Каждому мобильному назначается отдельный Частотный канал для продолжительности вызова
Достаточная защитная полоса требуется для предотвращения интерференции от соседнего канала
Как правило, мобильные терминалы имеют одну нисходящую линию связи полосы частот и одну восходящую линию связи полосы частот
Разные сотовые сетевые протоколы используют разные частоты
№9 слайд
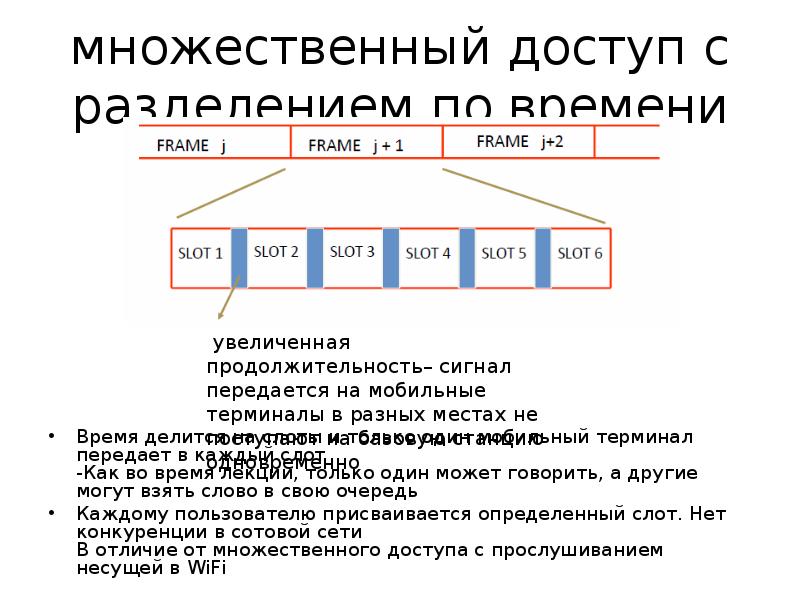

Содержание слайда: множественный доступ с разделением по времени
Время делится на слоты и только один мобильный терминал передает в каждый слот
-Как во время лекции, только один может говорить, а другие могут взять слово в свою очередь
Каждому пользователю присваивается определенный слот. Нет конкуренции в сотовой сети
В отличие от множественного доступа с прослушиванием несущей в WiFi
№10 слайд


Содержание слайда: множественный доступ с кодовым разделением
Использование ортогональных кодов для разделения разных трансмиссий
Каждый символ бит передается как большее число битов, используя пользовательский код – распространение
-Ширина полосы частот, занятой сигналом, намного больше, чем скорость передачи информации
Но все Пользователи используют ту же полосу частот совместно
№13 слайд


Содержание слайда: GSM услуги
Голосe, 3.1 kHz
служба коротких сообщений Short Message Service (SMS)
1985 GSM стандарт, который позволяет сообщения не более 160 символов. (incl. spaces) чтобы переть сообщения между телефонами и другими станциями
Over 2.4 billion people use it; multi-billion $ industry
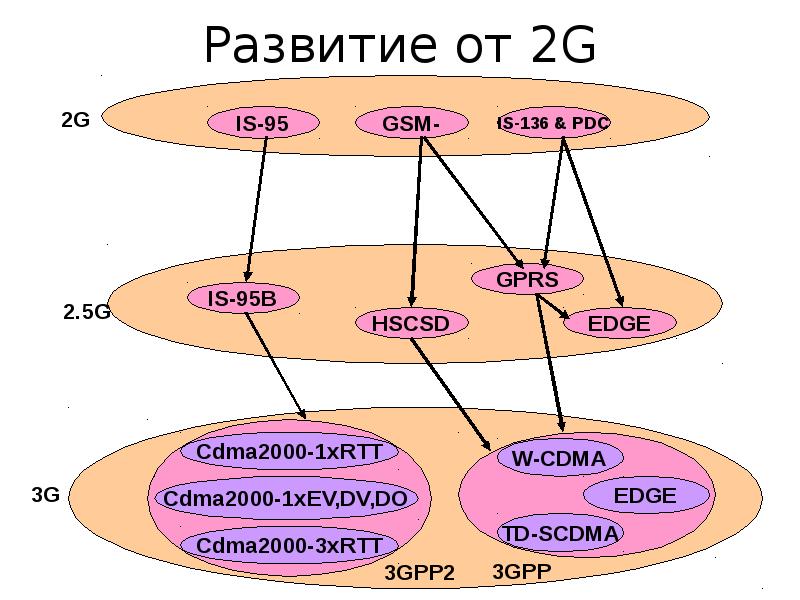
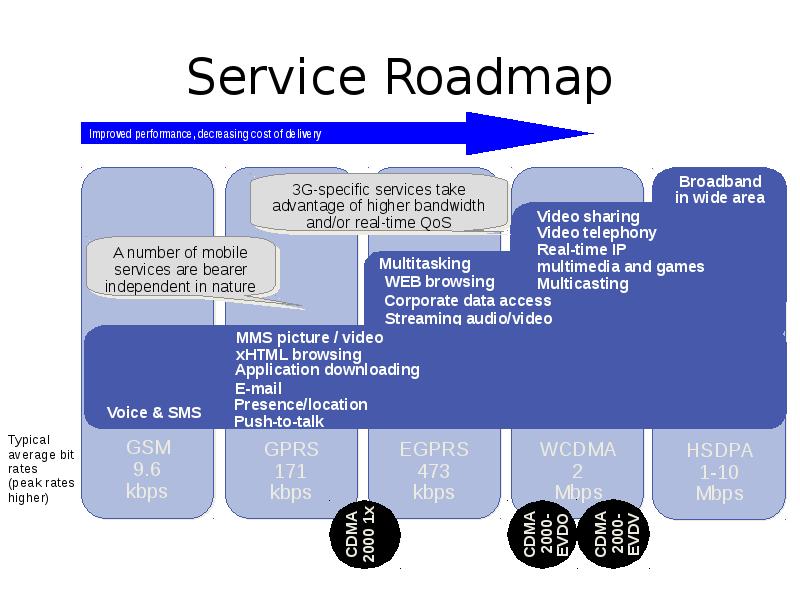
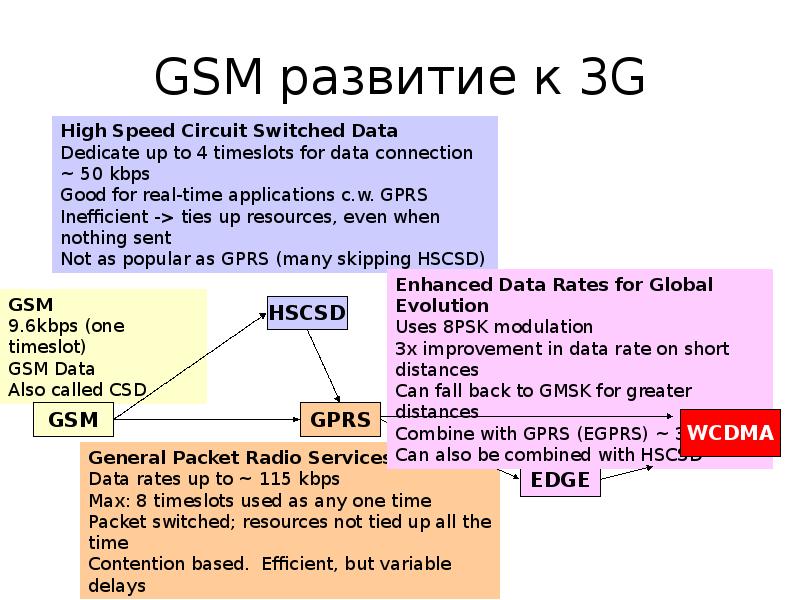
пакетная радиосвязь общего пользования General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
GSM upgrade that provides IP-based packet data transmission up to 114 kbps
Users can “simultaneously” make calls and send data
GPRS provides “always on” Internet access and the Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) whereby users can send rich text, audio, video messages to each other
Performance degrades as number of users increase
GPRS is an example of 2.5G telephony – 2G service similar to 3G
№18 слайд


Содержание слайда: Subscriber Identity Module
A small smart card
Encryption codes needed to identify the subscriber
Subscriber IMSI number
Subscriber’s own information (telephone directory)
Third party applications (banking etc.)
Can also be used in other systems besides GSM, e.g., some WLAN access points accept SIM based user authentication
№19 слайд


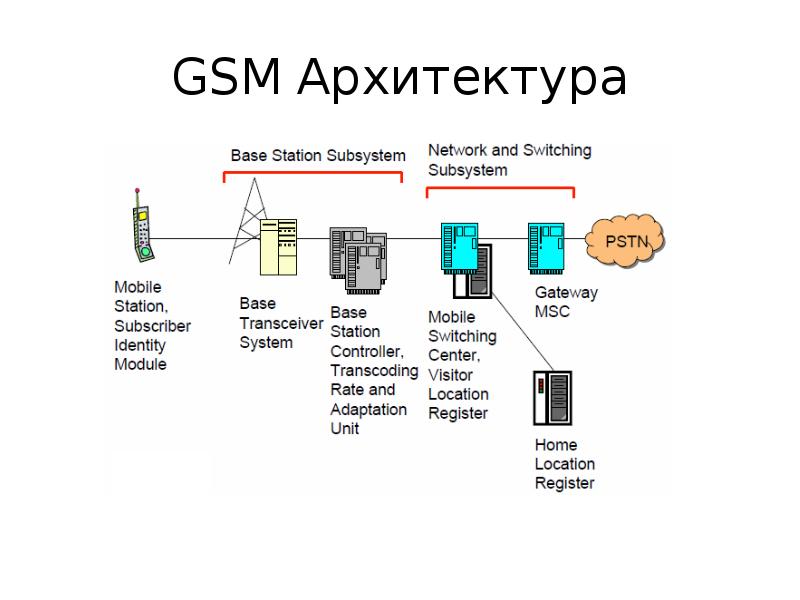
Содержание слайда: Base Station Subsystem
подсистема базовых станций
Transcoding Rate and Adaptation Unit (TRAU)
Выполняет кодирование между 64 кбит / с ИКМ кодирование используется в магистральной сети и 13 Кбит / с используется для кодирования мобильной станции (МС)
Base Station Controller (BSC)
Контролирует канал (тайм-слот) распределение осуществляемые BTS
Управляет хэндоверами в пределах BSS
Знает, какие мобильные станции в пределах ячейки и информирует MSC/VLR об этом
Base Transceiver System (BTS)
Controls several transmitters
Each transmitter has 8 time slots, some used for signaling, on a specific frequency
№20 слайд


Содержание слайда: Network and Switching Subsystem
подсистема сети и коммутации
опорная сеть GSM -телефонная сеть с дополнительными возможностями сотовой сети Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
В типичной телефонной станции (сети ISDN Exchange), которая поддерживает мобильную связь
Visitor Location Register (VLR)
A database, part of the MSC
Contains the location of the active Mobile Stations
Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC)
Links the system to PSTN and other operators
Home Location Register (HLR)
Contain subscriber information, including authentication information in Authentication Center (AuC)
Equipment Identity Register (EIR)
International Mobile Station Equipment Identity (IMEI) codes for e.g., blacklisting stolen phones
№21 слайд


Содержание слайда: Home Location Register
домашний регистр местоположения
One database per operator
Contains all the permanent subscriber information
MSISDN (Mobile Subscriber ISDN number) is the telephone number of the subscriber
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is a 15 digit code used to identify the subscriber
It incorporates a country code and operator code
IMSI code is used to link the MSISDN number to the subscriber’s SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)
Charging information
Services available to the customer
Also the subscriber’s present Location Area Code, which refers to the MSC, which can connect to the MS.
№22 слайд


Содержание слайда: Другие системы
Operations Support System Система Поддержки Операций
The management network for the whole GSM network
Usually vendor dependent
Very loosely specified in the GSM standards
Услуги с добавленной стоимостью
-Voice mail
Call forwarding
Group calls
Short Message Service Center Центр
Службы Коротких Сообщений
-Stores and forwards the SMS messages
Like an E-mail server
Required to operate the SMS services
№23 слайд


Содержание слайда: Смена Местоположения
При перекрытии сот мобильная станция может "видеть" несколько приемопередатчиков (BTSes)
МС отслеживает идентификатор для BSC контроля сот
Когда мобильная станция приближается в область новойBSC, она просит обновления местоположения
Обновления передаются на MSC, заносится в VLR, старая BSC уведомлена и подтверждение передается обратно
№24 слайд


Содержание слайда: Handoff (Handover)
When a call is in process, the changes in location need special processing
Within a BSS, the BSC, which knows the current radio link configuration (including feedbacks from the MS), prepares an available channel in the new BTS
The MS is told to switch over to the new BTS
This is called a hard handoff
In a soft handoff, the MS is connected to two BTSes simultaneously
№25 слайд


Содержание слайда: Roaming
When a MS enters another operators network, it can be allowed to use the services of this operator
Operator to operator agreements and contracts
Higher billing
The MS is identified by the information in the SIM card and the identification request is forwarded to the home operator
The home HLR is updated to reflect the MS’s current location
№31 слайд

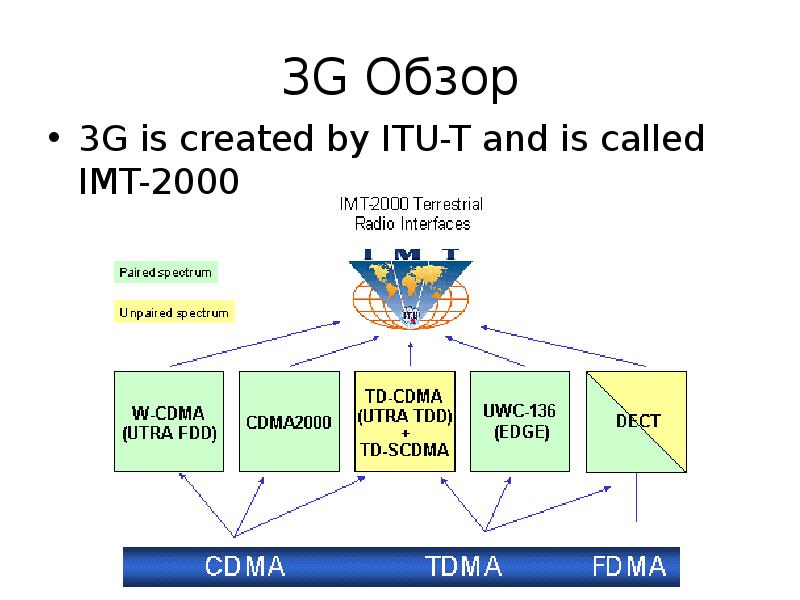
Содержание слайда: UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS)
UMTS is an upgrade from GSM via GPRS or EDGE
The standardization work for UMTS is carried out by Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)
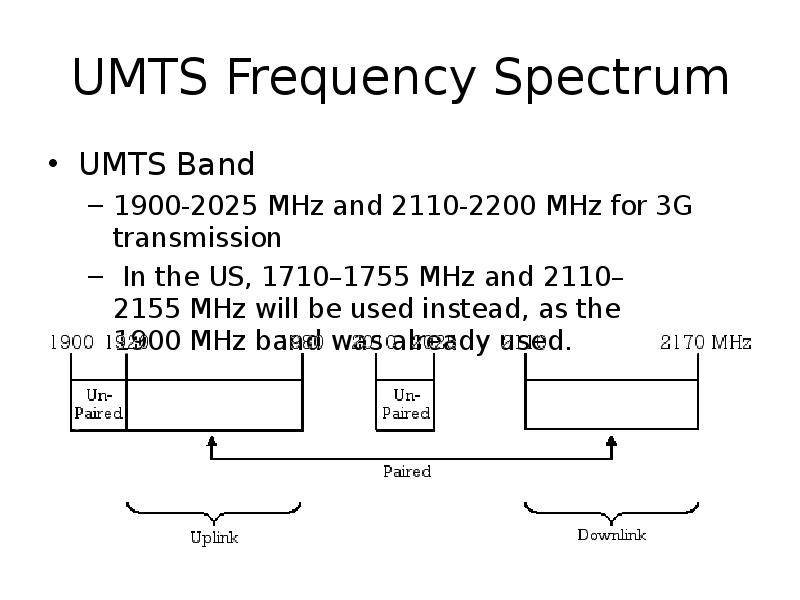
Data rates of UMTS are:
144 kbps for rural
384 kbps for urban outdoor
2048 kbps for indoor and low range outdoor
Virtual Home Environment (VHE)
№34 слайд
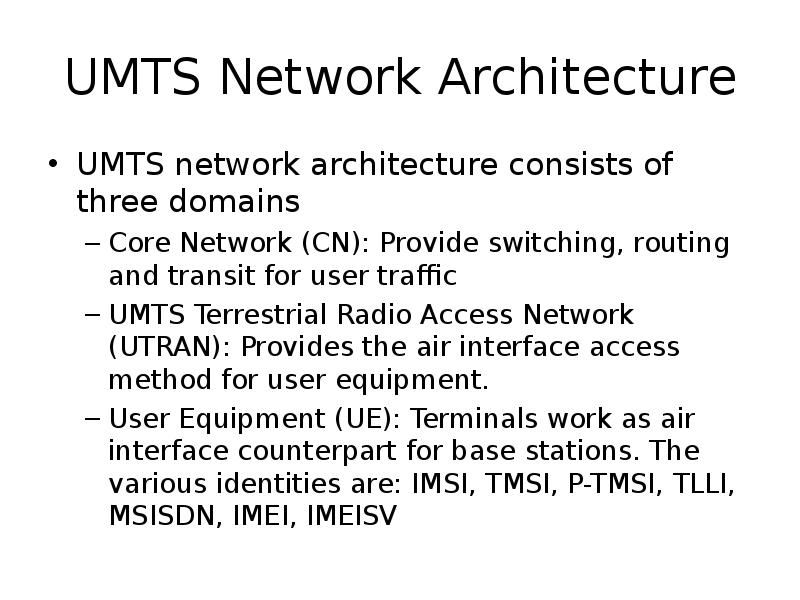

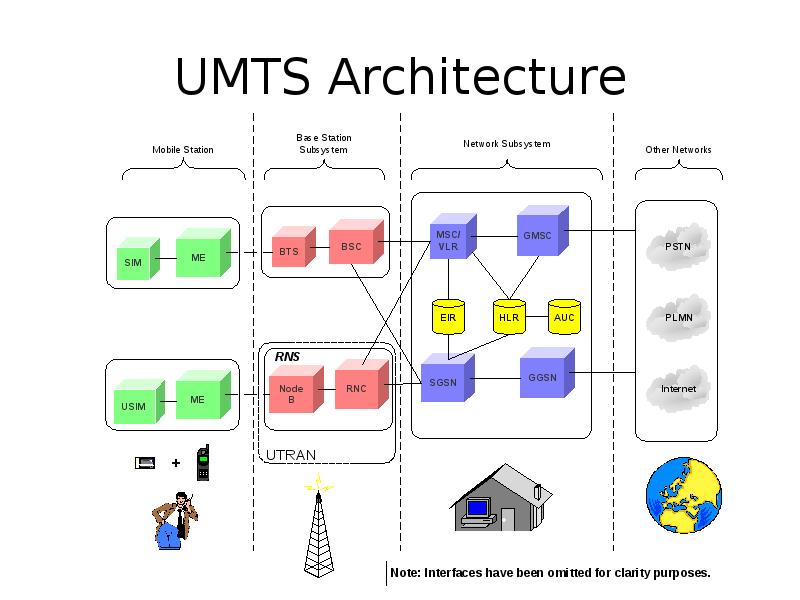
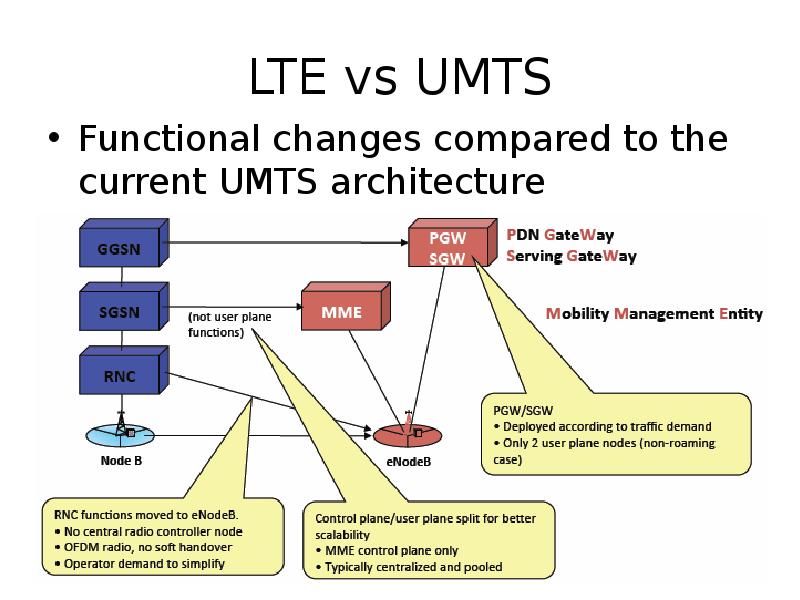
Содержание слайда: UMTS Network Architecture
UMTS network architecture consists of three domains
Core Network (CN): Provide switching, routing and transit for user traffic
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN): Provides the air interface access method for user equipment.
User Equipment (UE): Terminals work as air interface counterpart for base stations. The various identities are: IMSI, TMSI, P-TMSI, TLLI, MSISDN, IMEI, IMEISV
№35 слайд


Содержание слайда: UTRAN
Wide band CDMA technology is selected for UTRAN air interface
WCDMA
TD-SCDMA
Base stations are referred to as Node-B and control equipment for Node-B is called as Radio Network Controller (RNC).
Functions of Node-B are
Air Interface Tx/Rx
Modulation/Demodulation
Functions of RNC are:
Radio Resource Control
Channel Allocation
Power Control Settings
Handover Control
Ciphering
Segmentation and reassembly
№36 слайд


Содержание слайда: 3.5G (HSPA)
High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) is an amalgamation of two mobile telephony protocols, High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) and High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA), that extends and improves the performance of existing WCDMA protocols
3.5G introduces many new features that will enhance the UMTS technology in future. 1xEV-DV already supports most of the features that will be provided in 3.5G. These include:
- Adaptive Modulation and Coding
- Fast Scheduling
- Backward compatibility with 3G
- Enhanced Air Interface
№40 слайд


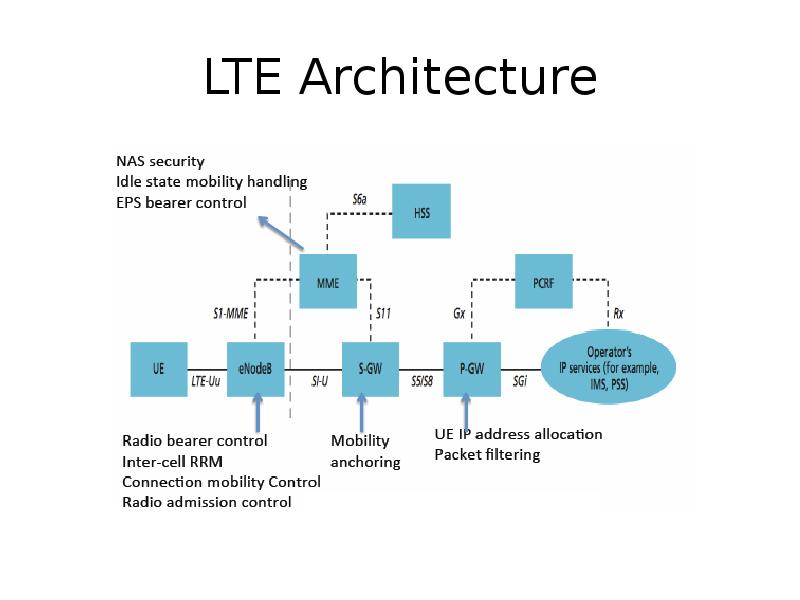
Содержание слайда: Major LTE Radio Technogies
Uses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for downlink
Uses Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) for uplink
Uses Multi-input Multi-output(MIMO) for enhanced throughput
Reduced power consumption
Higher RF power amplifier efficiency (less battery power used by handsets)
Скачать все slide презентации Мобильные сотовые сети одним архивом:
Похожие презентации
-
 Национальная программа развития сети автомобильных дорог в России
Национальная программа развития сети автомобильных дорог в России -
 Мобильные сети связи
Мобильные сети связи -
 Сети мобильной связи 1-го и 2-го поколений
Сети мобильной связи 1-го и 2-го поколений -
 Сети мобильной связи
Сети мобильной связи -
 Развитие сотовых мобильных телефонов
Развитие сотовых мобильных телефонов -
 Мобильные сети GSM. (Лекция 11)
Мобильные сети GSM. (Лекция 11) -
 АО «Ашасветотехника», производство взрывозащищенных, общепромышленных, автомобильных, железнодорожных и авиационных светильник
АО «Ашасветотехника», производство взрывозащищенных, общепромышленных, автомобильных, железнодорожных и авиационных светильник -
 Организация ведомственной документальной телеграфной связи с возможностью интеграции в мультисервисные цифровые сети (ip сети)
Организация ведомственной документальной телеграфной связи с возможностью интеграции в мультисервисные цифровые сети (ip сети) -
 Системы связи и сети передачи информации Виды модуляции сигналов. Детектирование
Системы связи и сети передачи информации Виды модуляции сигналов. Детектирование -
 Инженерные сети на строительной площадке
Инженерные сети на строительной площадке